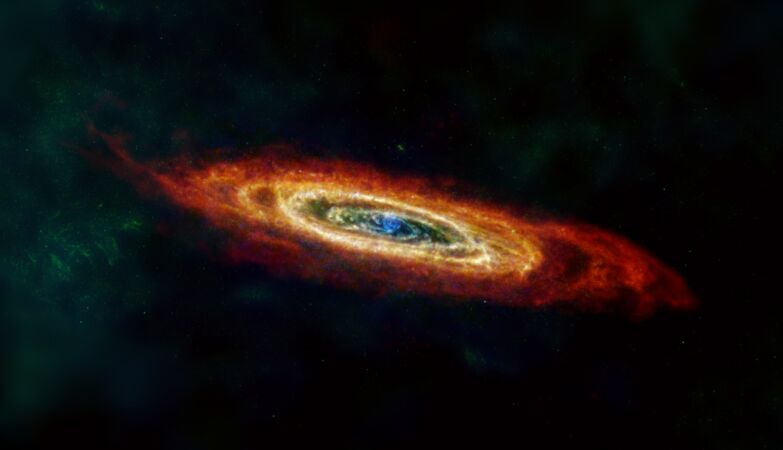
The Andromeda Galaxy, or M31, is shown here in infrared and radio.
Massive stars explode as supernovae at the end of their lives. The explosions, which leave behind a black hole or neutron star, are so energetic that they can outshine their host galaxies for months. Recently, a team of astronomers spotted a star that skipped the explosion and turned directly into a black hole.
In 2014, the supergiant star M31-2014-DS1located in the Andromeda galaxy, 2.5 million light-years from our planet, showed an intense brightness before gradually dimming between 2016 and 2023, and completely disappeared from the view of telescopes.
The star, with a mass 20 times that of the Sun, intrigued scientists because didn’t have the explosion of light typical of supernovae when they collapse.
This episode may, according to , represent a rare case of a “failed supernova”. This is the hypothesis suggested by a team of astronomers in a report available on arXiv, which still needs peer review.
“This dramatic and long-lasting disappearance of M31-2014-DS1 is an unusual occurrence in the context of massive stars”, reads the scientific article. “The absence of a visible explosion suggests the signature of a ‘failed’ supernova, in which the star’s core collapses directly.”
This image illustrates how the neutrino shock wave can stop, causing a black hole without a supernova explosion.
Stars like M31-2014-DS1 produce energy through nuclear fusion, converting hydrogen into helium. When the gas runs out, these massive stars begin to fuse heavier elements, until the core reaches a composition of iron, an element that does not release energy when it fuses.
At this stage, the internal pressure weakens and the star collapses under its own gravity.
When stars with more than eight times the mass of the Sun die, their outer layers are expelled in a massive explosion known as supernovawhich leaves behind a black hole or neutron star.
To investigate the mysterious phenomenon of “failed supernova“, in which some stars collapse directly into black holes, without emitting a visible supernova, the team analyzed data from NASA’s NEOWISE asteroid hunter, which observed objects in the Universe until it was deactivated at the beginning of the month.
In observations of M31-2014-DS1, experts noted its gradual fading between 2016 and 2019. In 2023, the star was already completely invisible.
With no signs of any explosion, they concluded that approximately 98% of the mass of the star collapsed into a black hole of approximately 6.5 solar masses.
The phenomenon was compared to the case of N6946-BH1another possible failed supernova identified in the galaxy NGC 6946, known as the “Fireworks Galaxy”.