We already know how the oldest representation of the sky was made: it needed 10 melting cycles at 700ºC before becoming the famous Nebra Disk, reveals a new study.
The Nebra Disc, considered the oldest representation of the sky still in existence, was subjected to a production process that involved approximately 10 hot forging cyclesaccording to a November 21 study in Scientific Reports.
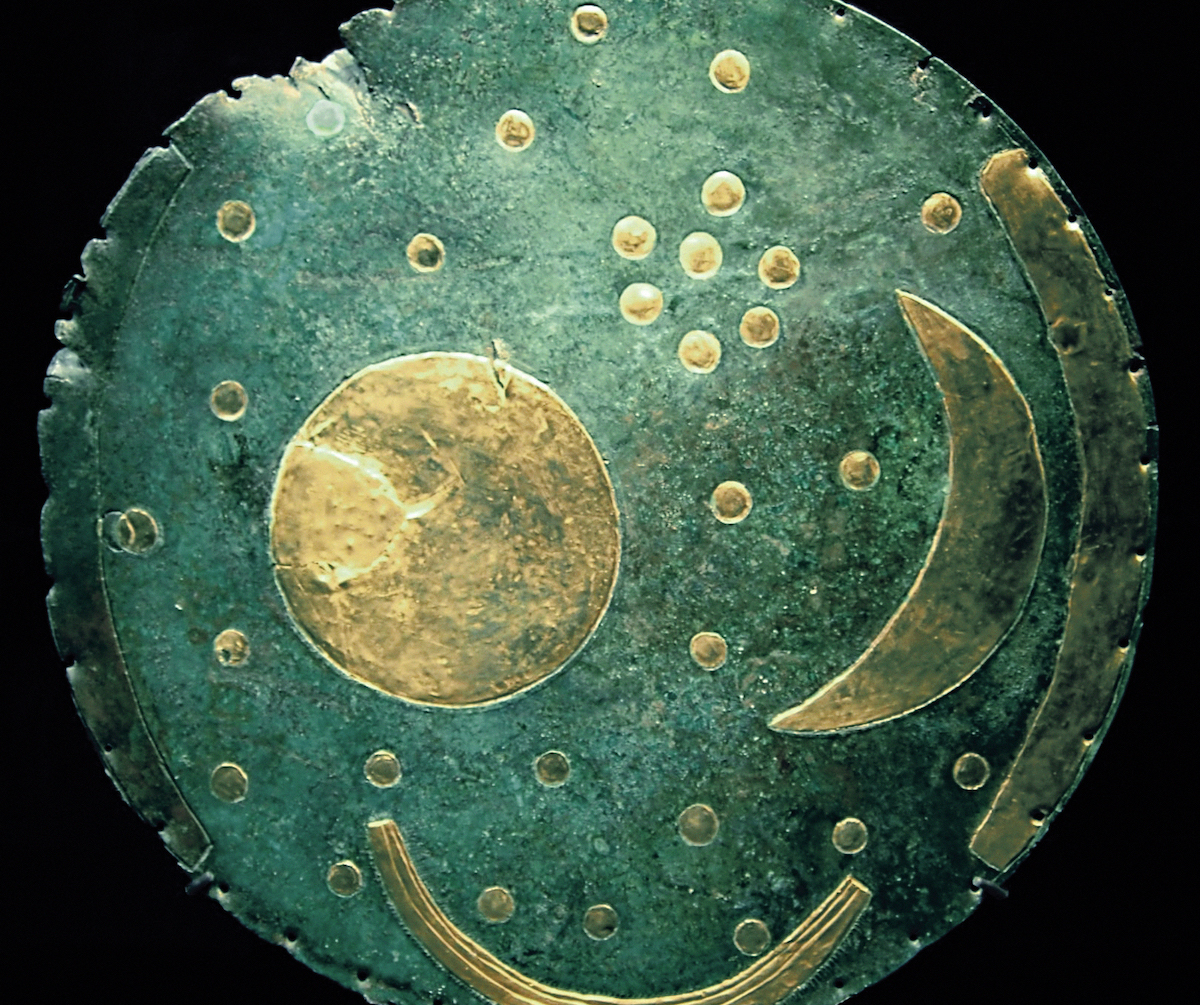
The Bronze Age artifact, designed with gold Inlaid as a representation of celestial objects, it highlights the remarkable skill of its creators, who probably attributed immense value to it.
Measuring 31 centimeters in diameter, the famous disc features representations of the Solyes crescent moonof stars and possibly a ship and the horizonte. It should be noted that a cluster of seven stars is believed to symbolize the , although its purpose — decorative, religious or none at all — remains uncertain.
Since its recovery in 2002, the Nebra Celestial Disc has been extensively analyzed and even added to UNESCO’s Memory of the World Register. However, the exact methods used to forge the artifact had eluded experts… until now.
A collaboration between archaeologists and metallurgists revealed that the disc was heated to 700°C about 10 times during its creation. In the Early Bronze Age, producing a fine, evenly wrought bronze object of this size represented a major challenge due to the limitations of metallurgical techniques at the time. Bronze, particularly the low-tin alloy used in the disc, did not have the fluidity necessary to form such a delicate shape in a single attempt.
Replicating the process, boilermaker Herbert Bauer demonstrated the immense effort involved in the process. Starting with a thick blank, he hammered and heated the bronze repeatedly, using progressively lighter tools, until the disc reached its final dimensions. Their findings confirmed that the original artisans would have followed a similar method, which required several cycles of forging.
Although the artifact is linked to objects dating back to 3600 yearsits exact age and the culture behind its creation remain a mystery. The record was stolen with unauthorized metal detectors in 1999, recovered in 2002, and studied along with other associated artifacts. Some researchers cited by argue that could be up to 1000 years younger than the conventional estimate.