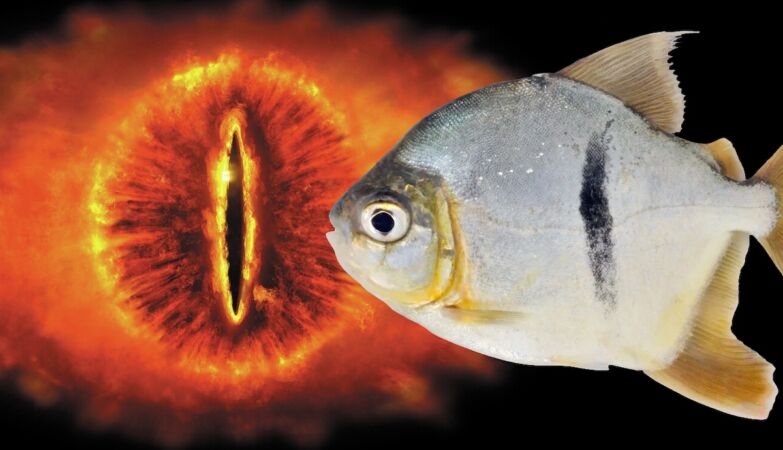
Specimen of Myloplus sauron with the Eye of Sauron in the background
As of last year, scientists estimate that we had discovered around 10% of the species on Earth. And in 2024 we meet some surprising species.
“Scientists estimate that we have identified only a tenth of all species on Earth,” he says Shannon Bennettchief of science at the California Academy of Sciences, in a statement to which he had access.
“While it is critical to protect known threatened species, we must also allocate resources to the identification of unknown species which can be equally important for the functioning of an ecosystem”, he further wrote.
In 2024, 138 new species were recorded. 32 are fish. One of the highlights was a pygmy seahorse called Cylix nkosi.
The seahorse relative was originally found in 2021 in the cool temperate waters surrounding New Zealand’s North Island, but the species this year was discovered in subtropical waters off South Africa, expanding this group’s known range into the Indian Ocean.
“South African reefs present notoriously difficult diving conditions, with bad weather and intense, choppy waves — we knew that we only had one dive to find her“, wrote the underwater photographer and marine biologist Richard Smith in another statement. And they found it.
“This species is also quite cryptic, the size of a tee golf, but fortunately we spotted a camouflaged female against some sponges about a mile offshore, on the sandy bottom of the ocean.”
The Natural History Museum in London was largely responsible for discovering new species. Will have done 190 new discoveries of living and fossilized animals, including 11 new species of moths, eight crabs, four rats and four snakes.
And some discoveries are a bit unusual. For example, one of the species of moths in a genus called Hemiceratoides, from Madagascarfeeds by drinking the tears of sleeping birdswhile another species of moth, Carmenta brachyclado, was found at flutter against a window in a living room in Wales, despite being originally from Guyana.
The moth got stuck in the trunk of a photographer who, unintentionally, brought the insect from South America to his home in Waleswhere it emerged. Your daughter, the ecologist Daisy Cadetrecognized the creature as something unusual and contacted the Natural History Museum in London.
There are also other bizarre cases, such as that of a vegetarian piranha named Myloplus sauron of the Xingu River, in Brazil, in a homage to the eye of Sauron from the book “Lord of the Rings”with whom the species had similarities, according to researchers.
“The reason we gave it this name was really obvious, because this fish is shaped like a disc and has a thin vertical bar along its body that resembles an eye,” he said. Rupert Collinsmuseum fish curator.
Additionally, in 2024, scientists documented a mysterious mollusk in the depths of the ocean, a ghost shark, a bubble-headed fish, and a type of semi-aquatic rat.
The Englishman also signs several discoveries — 149. One of them deals with Phellodon castaneoleucus, a fungus that has tooth-like structures instead of the typical gills.
And it’s not just the shark that is a ghost: a ghost palm treewith a gray stem and white underside.
The Royal Botanic Gardens also discovered a enigmatic family of plants known as Afrothismia which are confined to African continental forests without the capacity for photosynthesis.
“The simple privilege of describing a species as new to science is an emotion that few will have the opportunity to experience,” he said. Martin Cheek, Principal Investigator of the Africa Team at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
“Unfortunately, this pleasure is increasingly being overshadowed by many threats that plants face as a direct consequence of human activity”, he stated.
“The devastating reality is that, most of the time, new species are being found on the verge of extinction and it’s a race against time find them and describe them all”, he concluded.


