Nesvorný et al.
It is a huge shell localized confines of our solar system, and is the source of many comets. So far, we’ve never been able to look at its appearance, but a NASA supercomputer has managed to create a simulation.
Even at its current speed of about 1.6 million kilometers a day, NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft It will not reach the OORT cloud in less than 300 years And it will not leave it for another 300,000, explains the.
This is why the Southwest Research Institute team and the American Natural History Museum is so useful: we can’t, at least for now, be even close to seeing this cloud.
In total, it is thought that there are cold bilies floating in the depths of space, although we only see those that appear in the inner solar system as long-term comets.
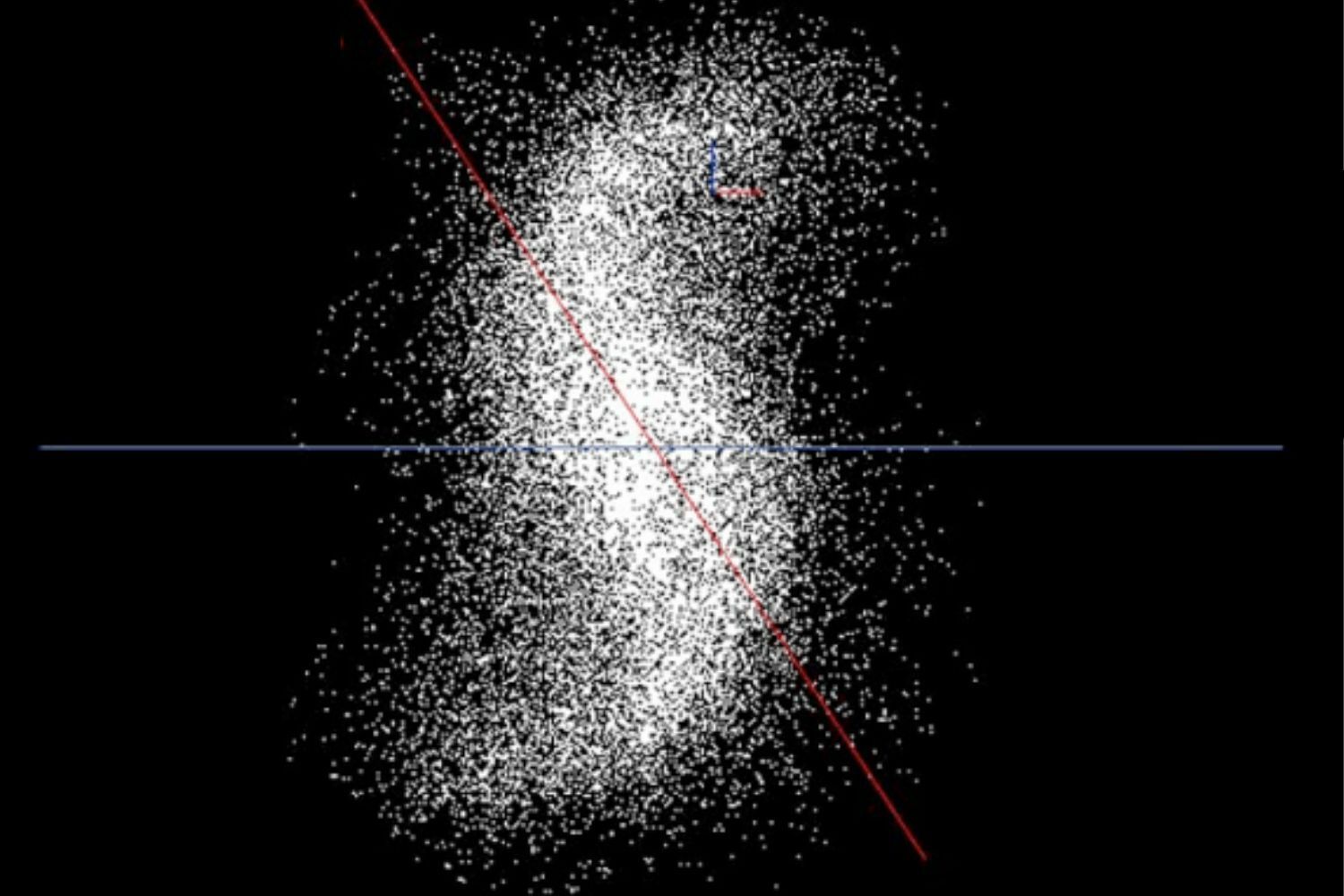
Researchers used information from the orbits of comets and gravitational forces inside and outside our solar system to build a model of the structure of this structure in the pleiades supercomputer. The result is a Bizarre spiral, with more spirals inside.
The Oort cloud has “armsThat extend for 15,000 UA from one end to the other. There is a cloud of “inner” OORT, considered slightly more populated than the “outer” Oort cloud, ranging from 10,000 to 100 000 UA.
One of the most curious aspects is the “Galactic Maré” – Stars, black holes and the center of our galaxy, have a crucial influence on the objects of the structure, but in the case of the objects closer to the sun, they are masked by the severity of our star.
In order to confirm this theory, it seems that we will still have to wait for a good decades-but NASA simulation can help us in the cosmic search for the habitat of any potential comets and its impact on us.