Next Friday, March 14, a total lunar eclipse will be visible from the middle of the world, from western Europe and Africa to the eastern extreme of Asia and Australia. It is a phenomenon that comes together in Spain, will begin during the twilight prior to dawn – especially 6:09, peninsular time -, so you can see its beginning but not its final part. The totality phase of the eclipse, in which the full moon adopts a reddish tone, will begin at 7:26. At that time, in the east peninsular and the Balearic Islands the satellite will have already been put, so it can only be seen as partial. On the other hand, in the center and west of the Peninsula, and in the Canary Islands, it can be seen as total before the moon is hidden under the horizon: that will happen after 7 minutes in Madrid, 27 minutes in A Coruña and 55 minutes in Santa Cruz de Tenerife.
and will coincide in the middle of the night, so it can be seen from beginning to end. The totality phase concludes at 8:31 and the partial eclipse ends at 9:47, Spanish peninsular time (1:31 and 2:47, respectively, in Mexico City).
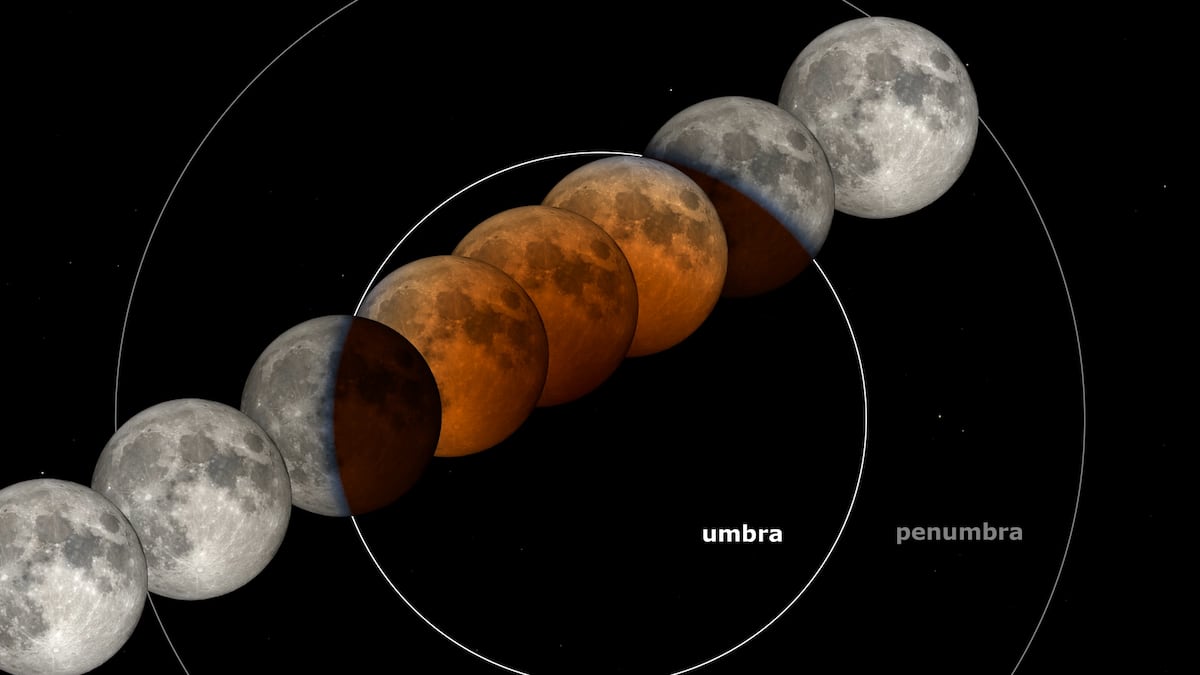
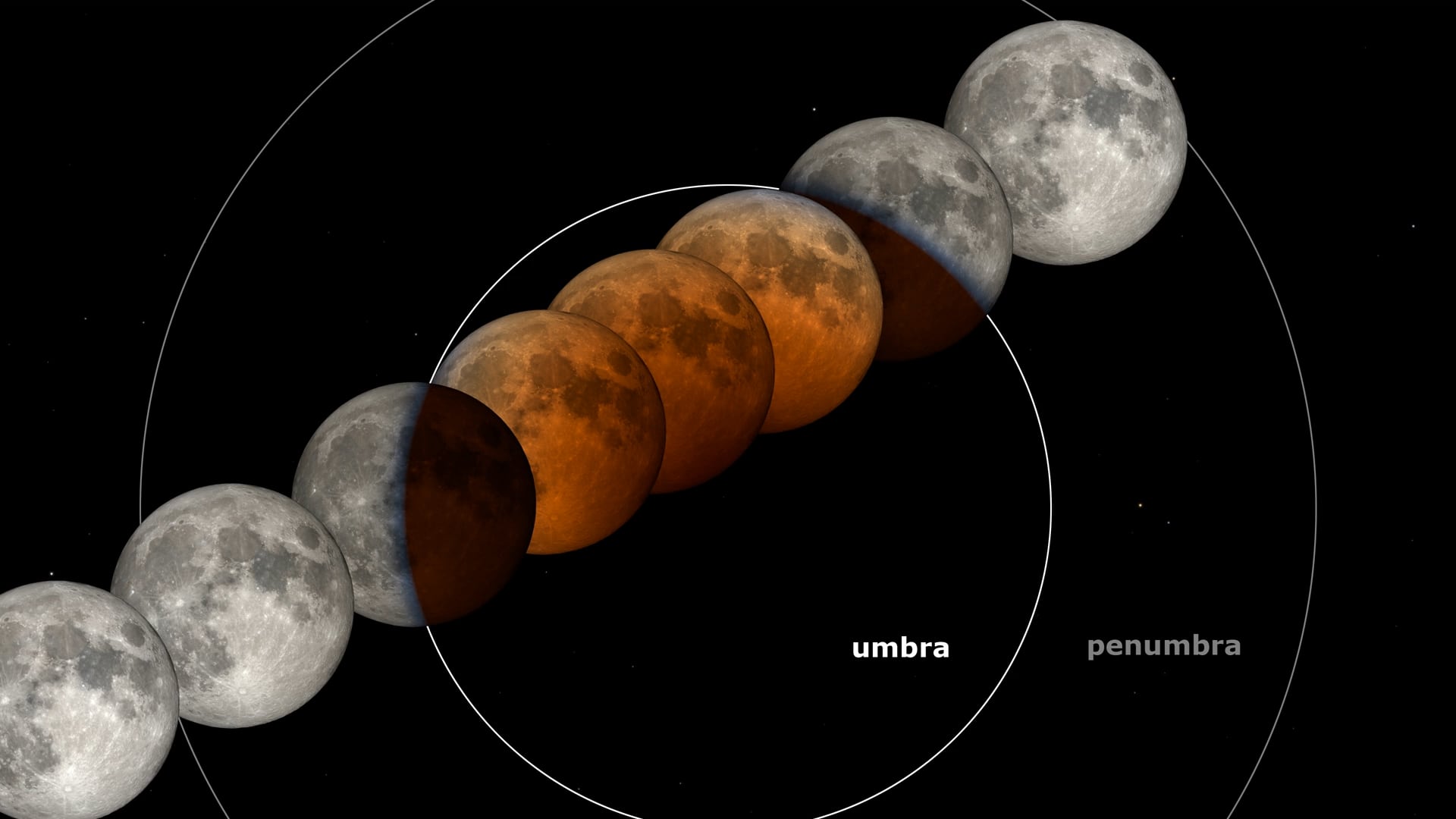
Javier Armentia, astrophysicist and professor at Pompeu Fabra University, explains that a lunar eclipse occurs when the sun, the earth and the moon are aligned in such a way that the moon passes through. In total lunar eclipses like next Friday – which always happens in the full moon phase – the whole moon passes inside the umbra, which is what is called the darkest part of the shadow. When the moon is inside the umbra, it looks like a reddish color. That is why lunar eclipses are known as “blood moons”, although the astrophysicist prefers to avoid that name. “It’s too sensationalist,” he says.
This phenomenon that stains The Moon is one of those responsible for the sky being blue or the orange sunsets. In the case of eclipse, the earth stands between the sun and the moon, blocking direct sunlight, but the earth’s atmosphere diverts and filters the light, dispersing the shortest wavelengths (blue and green) and allowing red and orange reds and oranges to illuminate the moon. As a result, the satellite acquires a coppery tone. “It is as if all the dawns and sunsets of the world are screened on the moon,” he summarizes. They also influence the amount of particles and dust present in the atmosphere during that time.
Armentia points out that the eclipse can be a. No special protection equipment is necessary or covering your eyes with specialized glasses to see it (as you have to do during solar eclipses). Although binoculars or a telescope will allow a better vision. A dark environment, away from the bright lights, offers the best conditions to witness the astronomical show.
Eclipse phases, minute by minute
whose phases occur simultaneously in the middle of the world in which at that time it is night. It is enough to subtract the time difference to know the schedule, which in the peninsular schedule of Spain will be the following:
04:57 – Beginning of the Penumbral Eclipse.
The moon enters the penumbra area, the outside of the shadow of the earth, and begins to darken with an effect that is still very subtle.
06:09 – Start of the partial eclipse.
The moon begins to enter the umbra – the darkest part of the shadow of the earth – and the partial eclipse begins. At first glance, it seems that the lunar album is missing a “bite.” With prismatic or telescope, it is observed how that part of the satellite inside the umbra looks very dark.
07:26 – Beginning of the totality.
The complete moon is in the earth’s umbra and dyes of coppery red. The use of prismatic or telescope for a better observation is recommended. In central and western Spain, the totality begins with the moon about to put on, at the edge of the dawn. In the east and the Balearic Islands, it will have already put on.
08:31 – Final of the totality.
The moon begins to get out of the umbra and the red color fades. The lunar “bite” begins to appear on the opposite side. The moon has already been put even in the westernmost part of Spain (the Canary Islands): at no point in the country the final part of the eclipse will be visible. However, all America can contemplate the initial, central and final part.
09:47 – Final of the partial eclipse.
The whole moon is again in the gloom of the earth, so that its darkening is already very subtle.
11:00 – Final del eclipse penumbral.
The eclipse is over.