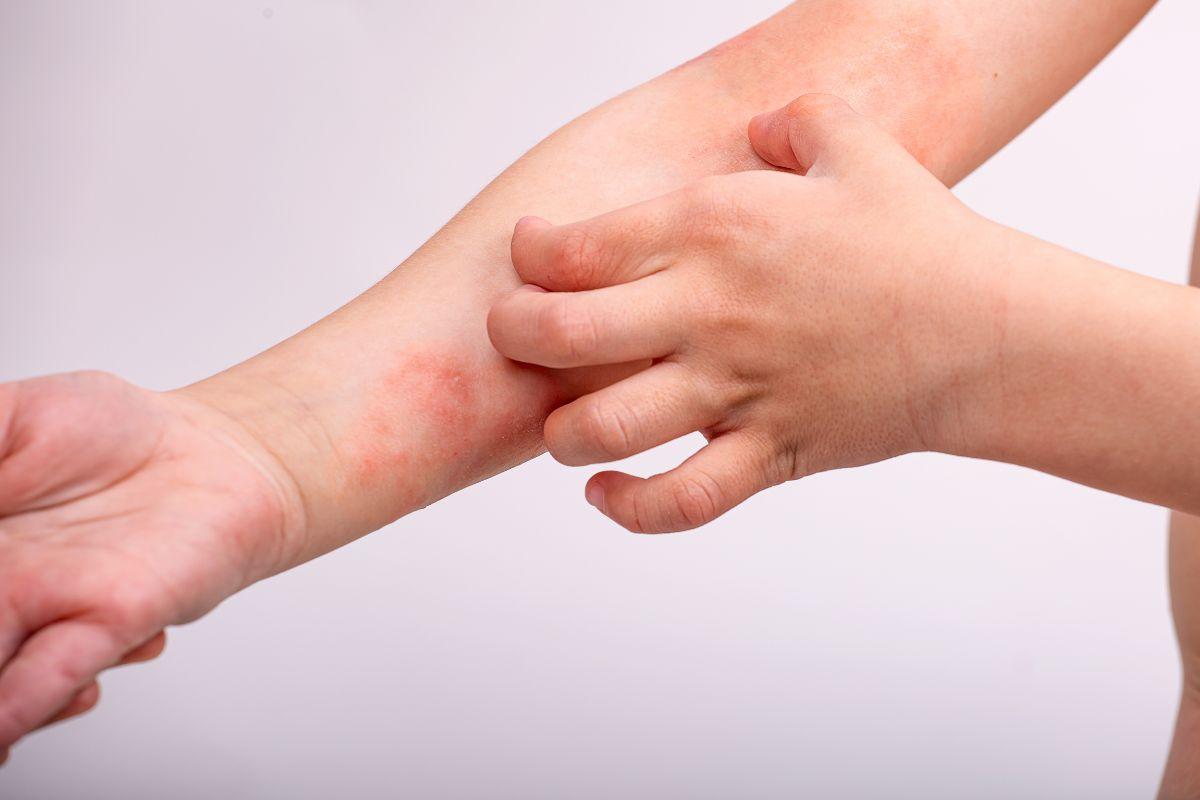
Eczema is a chronic skin disease, whose symptoms often become a serious challenge for both physical and emotional well -being. This condition affects 10 to 20 % of children and 2 to 10 % of adults worldwide. Although it may appear as simple, in fact eczema is a multifaceted, difficult problem that requires constant attention.
What is eczema?
Eczema is due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The skin of the sufferers is characterized by a weakened protective barrier, making the stimuli more deep and inflammation. The most common form is atopic dermatitis, but eczema includes other species.
The most common symptoms
The main symptom of eczema – persistent itching; If itchy rash is likely to be eczema. Other symptoms:
- dry, cracked skin;
- redness or darkening;
- scaling, cracks;
- swollen or blisters;
- skin thickening or nodules;
- deterioration at night, especially due to itching.
Where does eczema appear?
Children eczema usually occur on the cheeks, scalp, hands. Adults – on elbows, knees, neck, eyelids, hands and feet. In addition to physical symptoms, this disease often leads to anxiety, depressionreduced self -confidence.
Has eczema always reddened?
No. The color of the rash depends on the skin type: light skin for people – reddish red, darker – purple, brown or even gray. This sometimes complicates diagnosis, especially if your doctor is not familiar with various skin phototypes.
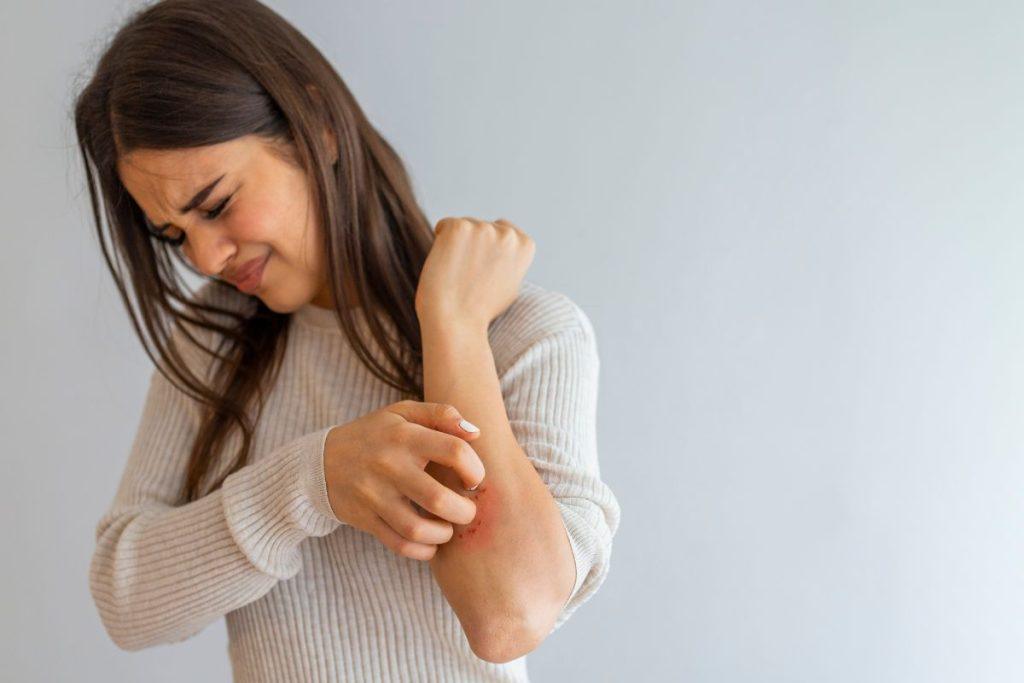

The effect of eczema on the quality of life
Extremely large – especially for sleep. Up to 90 % of patients indicate that itching is sleeping poorly. Frequent cases are bloody bedding from digging. Sports also cause problems as sweat irritates the skin.
What can cause exacerbations?
- stress (especially in adults);
- changes in temperature or humidity;
- pollen, dust mites, animal dandruff;
- aggressive cleaning agents;
- food (such as citrus, nuts, milk);
- woolen or synthetic clothing.
Stress is one of the strongest factors that weakens the immune system and skin protection.
Treatment and help
This disease is incurablebut it can be controlled. Treatment:
- odorless moisturizers;
- local corticosteroids;
- antihistamines;
- Immunomodulatory creams;
- Phototherapy;
- Biological drugs in severe cases.
How to help yourself at home?
- Take the Trigger’s diary – Helps to trace what provokes exacerbations.
- Daily moisturize the skin – Especially after bathing.
- Avoid hot baths.
- Choose gentle detergents and natural fabrics.
- Learn to relaxation methods – Meditation, breathing exercises reduce the effect of stress.
When do you go to the doctor?
- if the rash spreads or does not pass;
- if disturbing sleep;
- If signs of infection occur (pus, swelling, fever).
Eczema is not just an aesthetic or temporary problem. It is a serious chronic disease that requires comprehensive attention. Proper care, regular contact with a dermatologist and stress management can help live a full life without constant exacerbations.
Source: tsn.ua
Photos associative © canva.