Pramodh Chitral Chandrasinghe, et al.
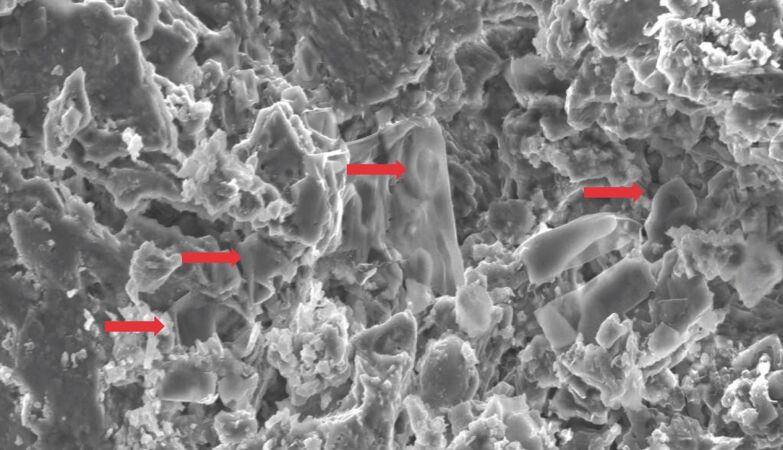
After all, soft tissues and cellular components may be preserved with old remains more often than we thought.
The herbivore dinosaur of duckboss, often nicknamed “Swamp Lizard”, scientifically Telmatosaurus transsylvanicus lived where the Romania currently is between 66 and 70 million of years ago.
Using Electronic Microscopy of High Resolution Shipping (Without), the researchers published in the Biology in April they identified low density characteristics that are remarkable to erythrocytes, or red blood cells, preserved in fossilized bone.
By identifying preserved proteins and biomarkers, scientists believe they can Get information about diseases that affected prehistoric creatures such as cancer. Discoveries can help scientists find out more details about this disease, and eventually help in the treatment of humans today.
The author of the study, Justin Stebbing, professor of biomedical sciences at Anglia Ruskin University, points to the relevance of the Study of soft tissues. “Dinosaurs, such as large and long life organisms, constitute an interesting case to investigate how species dealt with susceptibility and resistance to cancer over millions of years, ”he says to
“Proteins, particularly those found in calcified tissues like bone, are more stable than DNA and less susceptible to degradation and contamination. This makes them ideal candidates for the study of old diseases, including cancer, in paleontological specimens ”.
“Unlike skeletal structures, soft tissues contain proteins that provide molecular information capable of revealing biological mechanisms underlying disease,” he says.
“Our investigation, using relatively poorly exploited methods, invites aThe deeper exploration that may contain the key to future beneficial discoveries for humans. However, it is crucial that long -term fossil conservation efforts are coordinated, ensuring that future researchers have access to adequate specimens for advanced molecular investigations. ”


