Cuevas-Quiñones et al., Commun. Earth Environment., 2025
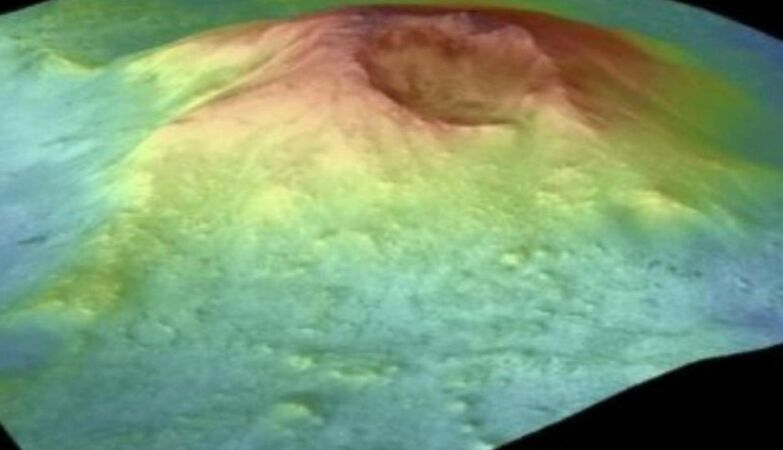
Volcano model Jezero Mons, in Mars
The volcano was discovered in the Jezero crater, which is one of the best known and studied regions of Mars.
Researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology have identified a volcanic structure in the Jezero crater in Mars, which could redefine the understanding of Martian geology.
The formation, now baptized as Jezero Mons, is located on the edge of the crater and occupies almost half of its widthwith significant implications for the study of habitability and chronology of the red planet.
O, published in Communications Earth and Environmenttreveals that Jezero Mons has characteristics compatible with a compound volcano: This revelation caught the scientific community by surprise, as this area of Mars has been widely studied.
The investigation was led by Sara C. Cuevas-Quinones, currently postgraduate student at Brown University, with the participation of teachers J. Wray, Frances Rivera-Hernndez and Jacob Adler.
“If only now we are identifying a volcano in one of the most studied areas of Mars, Imagine how much more they can exist”Said Professor Wray, highlighting the relevance of the discovery.
Although the mountain had already been observed in low resolution images in 2007, the focus of the time was Jezero’s aquatic past, namely the presence of an ancient lake. The perspective changed with the arrival of NASA’s Rover perseverance, which found unexpected evidence of volcanic rocks in the region.
The discovery was possible thanks to the participation of Cuevas-Quinones in a summer research program in Georgia Tech, where the team Reanaged data from various space missionsincluding Mars Odyssey, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, Exomars Trace Gas Orbiter and Perseverance itself.
Although it is not possible to confirm with full confirm the volcanic origin of Jezero Mons, the researchers stress that the structure shares many similarities to terrestrial volcanoes And Martians already identified, explains the.
The proximity between a volcanic system and an old lacustrus environment also raises the possibility of existence of hydrothermal systems In the past of Mars – places with the potential to support microbial life. In addition, samples of igneous rocks collected by perseverance may allow dating by radioisotopes if they are brought to the earth, helping to establish accurate dates in Martian geological history.
“The combination of housing sedimentary environments with scientifically valuable volcanic rocks makes Jezero even more fascinating“Concluded Wray.


