Deyanira Geisnæs Shave
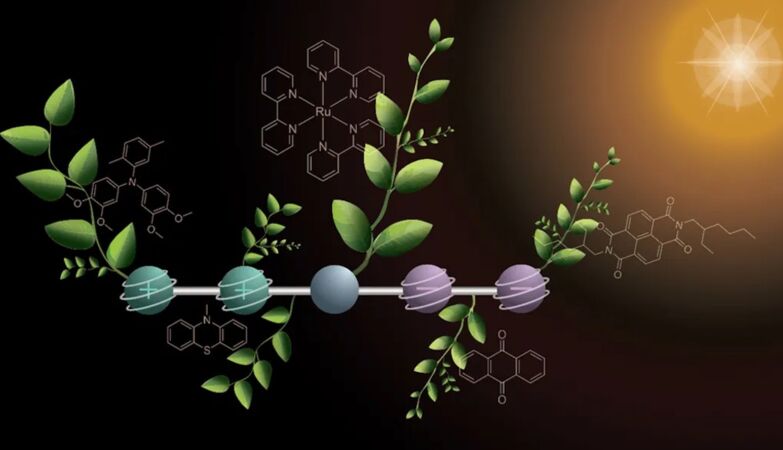
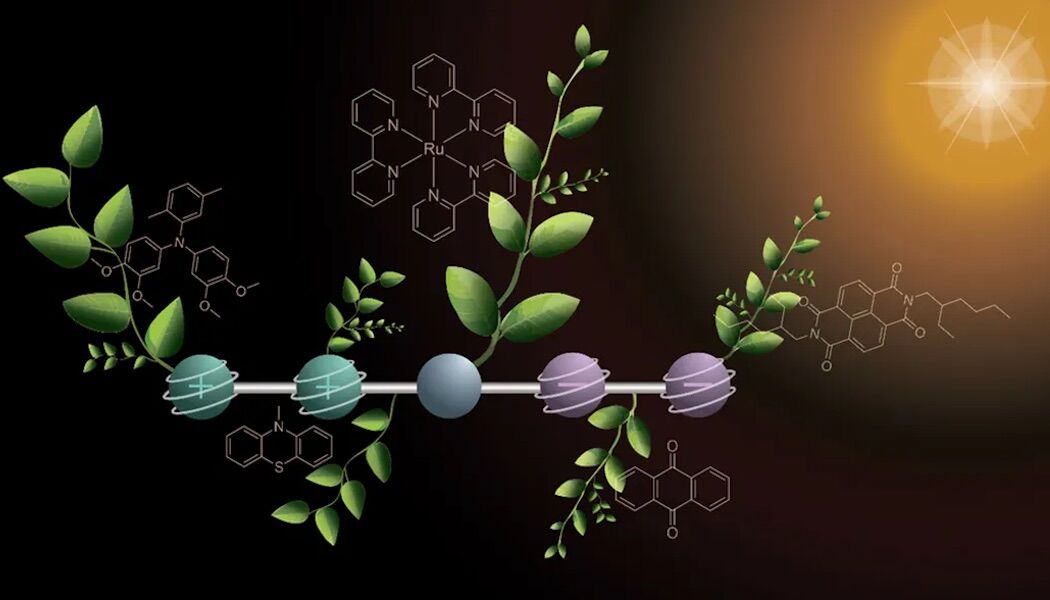
As with natural photosynthesis, the new molecule temporarily stores two positive charges and two negative charges.
A team of researchers at the University of Basel, Switzerland, created an essential molecule for the artificial photosynthesisthe process of conversion of sunlight into stored energy.
The discovery, presented in a published on Monday in Nature Chemistrysolves an important problem of artificial photosynthesis: the need for Store multiple loads.
The newly created molecule can simultaneously keep two charges positive and two negatives, in which researchers consider it to be a significant step towards sustainable energy.
A photosynthesis, the basis of most life on earthallows plants to transform carbohydrate carbon dioxide using sunlight.
This energy is then transmitted along the food chain when animals consume plants and other animals, releasing carbon dioxide back to the atmosphere in the process.
Modern industrial energy sources, however, generate huge amounts of carbon dioxidein a comparable mechanism to recycle it, leading to a excess greenhouse gases.
The University of Basel team intends nature Taking advantage of sunlight to produce high energy and neutral solar fuels in carbon, including hydrogen, methanol and synthetic gasoline.
The objective of the team of investigators, led by the teacher Oliver Wengerfrom the Department of Chemistry at the University of Basel, is replicate photosynthesisensuring that fuels release only both carbon and necessary to produce them.
Under light irradiation, the now created molecule successfully stored four loads, one crucial precursor to energy conversion. The next step will be use this energy stored to boost reactions such as water division into hydrogen and oxygen.
The molecule conceived by the study authors is composed of five parts connected, each with a specific function.
In its nucleus is a sEmission responsible for absorbing sunlight and start the electron transfer process. On one side, two units capture electrons and gain negative charges, while on the other, two segments release electrons, creating positive charges.
When exposed to a pair of flashes of light, the molecule produces the four charges in a two -step process.
The first impulse of light triggers the reactions generating energycreating a positive and negative charge, which then travel to the opposite ends of the molecule. With another flash, The reaction is repeatedcarrying the molecule with two negative charges and two positive.
“This gradual excitement makes it possible to use light sImprovely weaker. As a result, we are already approaching the intensity of sunlight ”, explains Mathis BrändlinPhD student at U.Basileia and first author of the study, in a statement published in.
“Previous investigations required extremely Fort laser lightAnd what was far from the view of artificial photosynthesis, ”says Brändlin.“ The loads in the molecule remain sufficient time to be used for other chemical reactions. ”
“We identified and implemented An important piece of puzzlewhich can help open new perspectives for a sustainable energy future, ”concludes Oliver Wenger.