Microsoft Designer / CCOPE
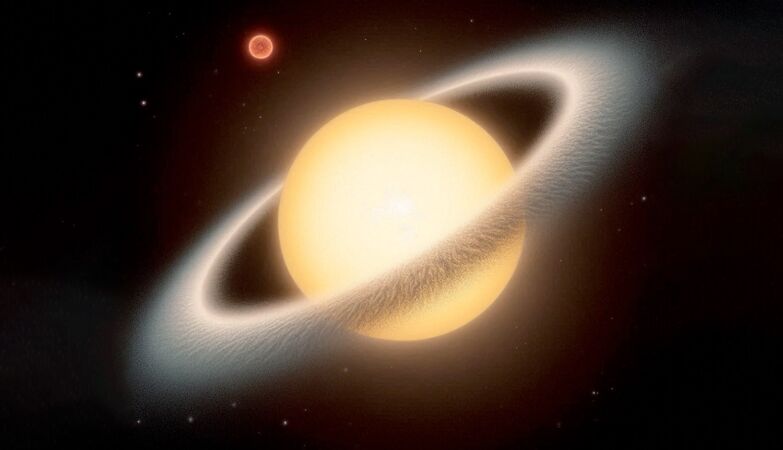
Illustration, created by artificial intelligence, of the possible aspect of the Asas-24FW system.
The stars die and disappear from sight at all times, but astronomers were intrigued when a star that had stable for over a decade almost disappeared for eight months.
Between the end of 2024 and the beginning of 2025, a star of our galaxy, designated by Assassn-24FWdecreased its shine by about 97%, before increasing again.
Since then, scientists have been exchanging theories about what will be behind this event rare and exciting.
Now an international team led by scientists at Ohio State University, USA, may have found a response to the mystery.
In a new recently published in the magazine The Open Journal of Astrophysics, Astronomers suggest that since the color of the star’s light remained unchanged during its darkening, the event was not caused by any evolution of the star, but by A large cloud of dust and gas around the star, which hid the view of the earth.
“We have explored three different scenarios for what could happen,” he said Raquel Foré-Toribiomain author of the study and postdoctoral researcher in astronomy. “Evidence suggests that there is likely that there is a disk -shaped dust cloud around you.”
Asas-24FW is a Class Star F -A little more massive star than our sun and about twice the size-and is located about 3000 light years from Earth.
Researchers estimate that the disk cloud that the surroundings have about 1.3 astronomical units (UA) in diameter, an even greater distance than the one that separates the sun from our planet (1 AU is the distance between the center of the Earth and the center of the sun).
Researchers suggest that this disk is also probably made up of Large carbon clusters or cold waterwith dimensions close to those of a large grain of dust found on Earth.
This material is sufficiently similar to planetary training discs so that your study can give astronomers new knowledge about stellar formation and evolution.
However, these discoveries in themselves do not explain all the anomalies of the system, said Forés-Toribio. Instead, researchers think that a smaller and colder star can also orbit Asas-24FW, which would make it a hidden binary system.
“At this moment, with the data we have, what we suggest is that there are two stars together in a binary system,” said Forés-Toribio. “The second star, which is much weak and less massivemay be provoking changes in geometry that lead to eclipses. ”
Although obscure systems like what the team saw are scarce, this rare eclipse was especially dramatic, he said Chris Kochanekstudy co -author and astronomy teacher, because when researchers sought similar objects, they could not find any that fit exactly in the same standard.
“We expected to find some similarities and we didn’t find many, which is interesting in itself,” said Kochanek. “But the hope is that, as we are finding more in the future, some standards can eventually be revealed.”
The system was discovered under the ASAS-SN (All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae) project, a network of small telescopes that monitor the entire visible night sky. Since its inception, more than a decade ago, Asas-SN has gathered about 14 million cosmos images.
“The ability of the universe to surprise us is continuous,” said Krzysztof Stanek, another study co -author and astronomy teacher. “Even with small telescopes on the ground and large telescopes in space, whenever we have a new capacity, we continue to discover new things.”
According to the team, the ASASSN-24FW system should go through a eclipse approximately every 43.8 yearsthe next one should only occur around 2068.
Although some team members will not expect to be around to study this event, they expect the work they left in the development of these long -term sky surveys give future scientists a foundation for making all kinds of new and exciting discoveries.
“We want our data to be accessible in a hundred yearsEven if we are not here, ”said Stanek.” The main goal of Asas-SN is that if something happens in heaven, we will have historical data about it. “
However, the team wants to use larger telescopes, such as the James Webb space telescope and the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT), to make more complete observations of the system as it returns to total shine.
“This study is a particularly interesting example of a wider class of Objects still very strange“Stanek said.” We learn more about astrophysics when we find things that are unusual, because it proves our theories. “


