TikTok / shlbmrtn
Big babies are healthy in most cases, but some health care can help you avoid having to perform interventions during birth to give birth to these “mini giants”.
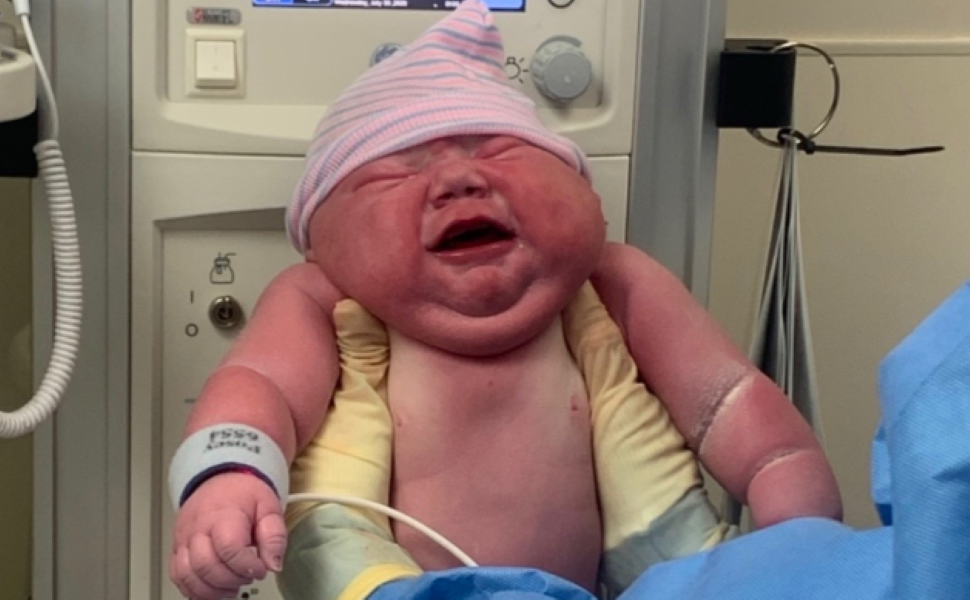
Baby Cassian has become an internet sensation. He was born this year, in the United States, weighing 5.8 kilograms. But after the mother and the hospital shared the news recently, it didn’t take long for headlines about the “giant baby” to spread around the world.
Although baby Cassian was born heavier than normal, it is not a unique case. There were other similar examples in the news — such as a baby born in Brazil in 2023, who weighed 7.3 kg.
These stories can make women all over the world cross their legs. But after all, how common are big babies and is childbirth always complicated?
What are big babies?
The term macrosomia describes babies who are born weighing more than 4 kg or 4.5 kg, depending on the definition used.
A large baby can also be defined as one who weighs more than the 90th percentile for their gestational age — i.e. More than 90% of babies are underweight at this stage of pregnancy. The term “large for gestational age” is probably more accurate, as it considers weight in conjunction with weeks of gestation.
Over the past decade, the percentage of large babies has remained stable in Australia — around 9–10% of births.
What are the risks for big babies and mothers?
We do not know the specific circumstances of Cassian’s birth, nor his or his mother’s health status. But, in general, the risk of complications increases when the baby is large — especially above 4.5 kg — although this does not always happen.
There may be a greater need for birth interventions, such as forceps, suction cups or cesarean sections. These interventions can affect a woman’s recovery and influence options for the next birth.
For the baby, there is an increased risk of shoulder dystocia — when the shoulders become stuck in the birth canal. In these cases, midwives or obstetricians may need to perform special maneuvers to free the baby, such as trying to lower one of the shoulders.
These maneuvers, although rare, can cause injury or lack of oxygenrequiring resuscitation of the newborn. However, these are uncommon complications and can occur even when the baby’s size was not expected.
What leads to the birth of giant babies?
In most cases, big babies are healthy, and there are several possible reasons:
- Genetic factors: Some families have a natural tendency towards big babies.
- Prolonged pregnancy: Babies who live past their due date tend to be larger.
- maternal diabetes, especially if poorly controlled, it can result in larger babies, as the excess sugar in the mother’s blood provides extra energy to the baby, which stores it in the form of fat.
- Gestational diabetes (diagnosed during pregnancy) increases the risk of the baby becoming obese or developing diabetes in the future.
- High maternal weight before or during pregnancy can also contribute to your baby’s size, often due to an increased risk of diabetes and possibly less healthy food choices.
What can women do?
The best health advice is to try to achieve a healthy weight (BMI less than 30) before pregnancy.
During pregnancy, maintain a balanced dietavoid foods and drinks rich in saturated fats and sugars, do not gain excess weight and exercise regularly. Speak to your midwife or obstetrician for support and guidance.
If you have diabetes (pre-existing or gestational), it is essential to closely monitor the baby’s blood sugar and growth.