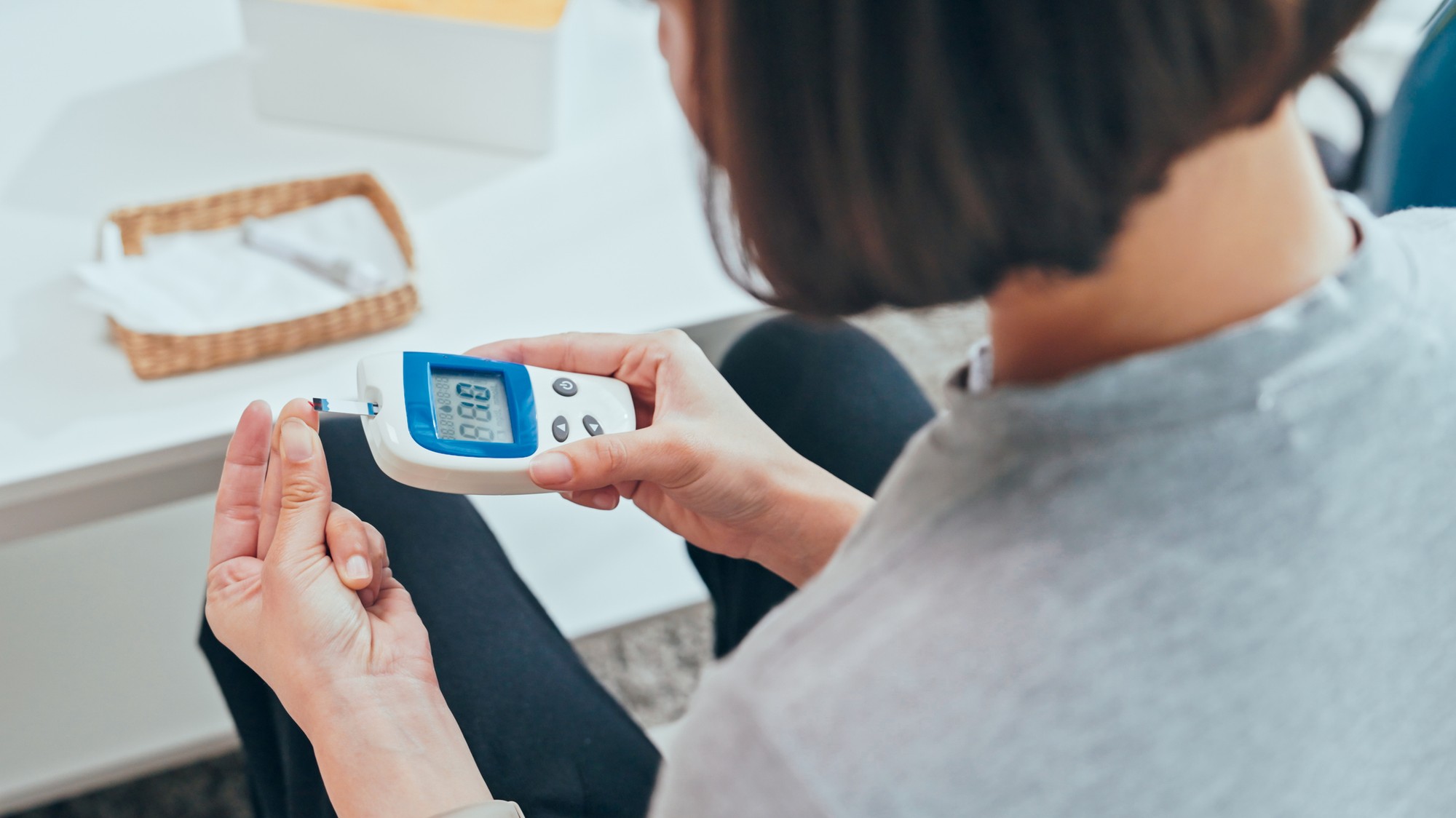
Diabetes has a special nature – it can completely change your life, but it often comes quietly and unobtrusively. According to data from the National Center for Health Information (NCZI) from October this year in Slovakia, the number of newly diagnosed with so-called diabetes in adults decreased by 14.5% year-on-year. By the end of 2024, they were monitoring 348,362 people in diabetes clinicscompared to 2023, the number of long-term monitored patients under the care of diabetologists increased by 3%.
In 2024, the largest part of patients were people with type 2 diabetes mellitus, which accounted for 90.9% of cases (316,716 people). Type 1 diabetes mellitus was diagnosed in 7.6% of patients (26,505 people). Gestational diabetes mellitus represented 0.9% (2,984) and the rest of the patients had other types of diabetes (2,157).
According to current IDF data, over 11 percent of adults (20-79 years old) live with diabetes and four out of ten people do not know about their illness. It is responsible for over 12% of global healthcare spending and the current trend is towards more than 850 million diabetics in 2050. “Prevention is important at any age. I also meet young adults and teenagers who already have type 2 diabetes,” points out Dr. Christophe Kosinski, deputy head of the Department of Endocrinology, Diabetology and Metabolism at the Geneva HUG.
While type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that destroys insulin-producing cells, Type 2 diabetes is mainly caused by a lack or reduced effectiveness of insulin – often associated with being overweight and having a sedentary lifestyle.
According to Dr. According to Kosinski, everyone should have their first preventive blood glucose test at the age of 35, and if the results are normal, the test should be repeated every three years. “The earlier pre-diabetes or diabetes is caught, the easier it is to treat – and in some cases, it’s possible to get back to normal,” he adds.
Social networks are flooded with advice on how to prevent blood sugar fluctuations with food or habits. Various influencers are persuading people to drink apple cider vinegar before meals or to start a meal with vegetables. However, doctors warn against blindly following such trends. Although some of the influencer tips are based on real scientific knowledge, they were often originally intended for patients with type 1 diabetes. However, this does not mean that everyone should follow them exactly. These 5 habits are essential to prevent type 2 diabetes.
Increase your fiber intake
Nutrition specialists point out that when discussing modern dietary trends, we often forget the basic principles of healthy nutrition. As reminded by Dr. Kosinski, it’s important prefer a balanced diet rich in fiber and complex carbohydrates – i.e. whole grain pasta, rice, bread or legumes. According to experts, fiber has a dual effect: it increases the feeling of satiety, thereby limiting sudden cravings and overeating, and at the same time it slows the rise of blood sugar.
This is also why the well-known popularizer of nutrition Jessie Inchauspé recommends start the meal with vegetables. However, according to nutritionist Isabelle Zanella-Ayer, this is not a new thing, but a long-known principle. In particular, a sufficient amount of fiber is key – that is, approximately 30 grams per day and five servings of vegetables, salads and fruit.
Don’t overdo it with protein
In recent years, high-protein diets and protein-enriched foods have come to prominence – especially powders and bars, which are popular among athletes, but this trend may not be beneficial for everyone. “High-protein diets are all the rage, but they can have harmful effects,” says Dr. Kosinski.
In healthy adults, when our intake exceeds our needs, protein is stored as fat. And that’s not ideal, because being overweight is one of the risk factors for type 2 diabetes. The expert warns that excess body fat, especially visceral fat, promotes inflammation in the body and can lead to insulin resistance. Muscles absorb sugar worse and need more insulin to work effectively. The pancreas therefore has to increase its production and in the pre-diabetes stage we observe hyperinsulinism.
The fight against a sedentary lifestyle
“When it comes to diabetes, physical activity is the real cure,” says Dr. Konsinski, pointing out that the WHO recommends 150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, or 75 to 150 minutes of vigorous activity. Unfortunately, 31% of adults and 80% of adolescents do not follow these recommendations.
According to the diabetologist, it is therefore essential to at least reduce the amount of time spent in inactivity. “Since most people cannot meet the official recommendations, the most important thing is to reduce a sedentary lifestyle. Any opportunity to take a walk, take the stairs or work in the garden can be especially meaningful for people with diabetes or pre-diabetes. Movement improves the muscles’ ability to absorb sugar, which reduces glycemic peaks,” he explains.
Enjoyment is also important
It should also be added that diabetes should be prevented does not mean completely avoiding all sugars. Glucose should not be demonized, as it is the main source of energy for the body and brain and we cannot function without it.
“Even when it comes to fast sugars, which we should avoid most of the time, we can sometimes indulge in a few excesses to preserve the enjoyment of food. If we avoid all potentially hyperglycemic foods, caused frustration may turn out to be harmful in the medium term,” warns the doctor.
According to Isabelle Zanella-Ayer, when you follow the food pyramid model, you see that there is still a little room at the very top for one fatty or salty treat a day. The concept of pleasure is important, but just because you like something doesn’t mean you have to eat it every day.
Better stress management
In addition to being overweight, an unbalanced diet and a sedentary job, risk factors for type 2 diabetes also include: age, genetic predispositions, high blood pressure, smoking and stress. By increasing the production of hormones, including cortisol and adrenaline, it can actually increase blood insulin levels, which can facilitate insulin resistance.
In case of stress, the body has the impression that it needs a quick source of energy, so it spontaneously releases sugar. Not to mention that stressful situations lead us to choose foods that are too fatty or too sweet.
This article comes from the Ringier publishing partner website. The content and data contained in it were taken without editorial intervention.