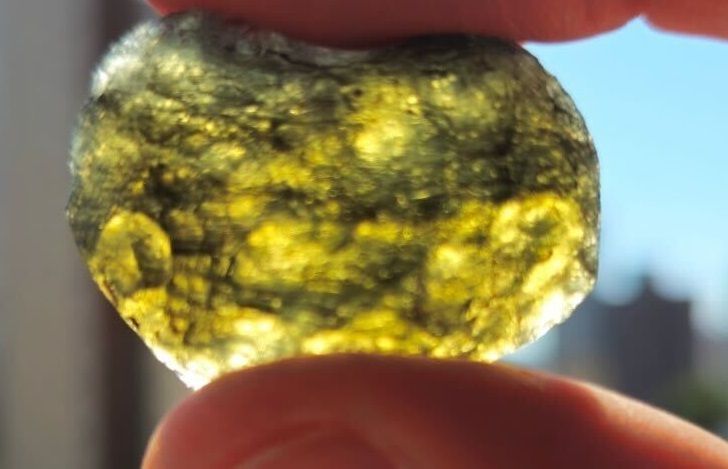
An object from space collided with Earth around six million years ago, scattering fragments across Brazil. Only now, in 2026, has science managed to confirm the event, which gave origin of pieces of glass known as tektites.
The discovery was made by geoscience researchers at Unicamp (State University of Campinas), reviewed and published in the journal Geology.
They were carried out studies to confirm the extraterrestrial origin of the material that helped to forge this glass.
“It was our first analysis. Precisely trying to separate it from another type of glass. Tektites also have their own chemical and physical-chemical characteristics. By analyzing this material, we can now separate it from another type of natural glass, very common, volcanic glass. They look similar, but chemically they are different”, reveals Álvaro Penteado Crósta, geologist at Unicamp, leader of the research, in an interview with CNN Brazil.
Remember the history of accidents in Alcântara; base has existed since 1983
Only five other places with this type of material have been proven by science around the planetpoints that range from Oceania to Europe, but this is the first time that the record has taken place in South America.
So far, no crater that emerged from the impact has been proven, more scientific studies need to be done. The research revealed only traces of this material, which, when touching the Earth’s soil, in contact with existing rocks, formed this type of glass.
Extent of Impact
For the researcher, it remains to find out what type of material it was, whether it was one or something gigantic like an asteroid, considering that the area of The extent of the remains found is more than 900 km²going from the north of Minas Gerais, where the research began, to the state of Piauí. It is believed that the impact was frightening on the Brazilian continental plate.
“On Earth, this type of shock will produce earthquakes that go beyond the Richter scale, in addition to producing a rain of fragmented material, a shock wave, and a sound wave”, analyzes Crósta.
At the time, the formation of the continents had practically the original shapethe African continent had already moved away from Brazilian territory and the formation of the Atlantic Ocean was practically consolidated.
The professor responsible for the research added how it was possible to address the temporal issue of glass formation. “This age is one of the results we get from the geochemical analysis. They are actually isotopes, which give us the precise age of when the rock was melted. From this fusion, this melting, this isotopic clock resets and starts counting; We then know exactly how old it is”, concludes the geologist.